Date: Dec 05, 2022 Read: 12501
Share:




For SSD serving as a data storage device, the security of data storage is very important. To protect the data from being stolen or tampered, SSD often encrypts the data. This paper will discuss the data encryption technology.
Data is encrypted mainly at host and in disk.
I. Host encryption
Host encryption refers to off-disk encryption, including software encryption, security authentication and hardware encryption.
1. Software encryption is done generally by Microsoft Bitlocker and Chinasec. Bitlocker is a computer-based local disk encryption tool that comes with VISTA operating system, which enhances security by encrypting all contents (data, APPs, and even Windows itself) on the hard disk; while Chinasec is a network- and data-based security manager, providing system data protection, document encryption and other overall solutions in traditional PC and mobile terminals by means of authentication, encryption, monitoring and tracking.
2. Setting a Windows login password by users is the most common way of security authentication. The system identifies users by passwords, thus ensuring the security of data in the computer.
3. Hardware encryption is done by TPM that is a hardware encryption template. It processes the encryption key in the device through the special security hardware integrated in the device and built with encryption algorithms such as RSA/AES/SHA. Many notebooks are designed with a TPM chip module to enable data encryption, password protection and other security functions, with the application performance superior to the above two.
II. Disk encryption
Disk encryption covers five ways of encryption: symmetric encryption and asymmetric encryption, ATA security, TCG, and hidden partition.
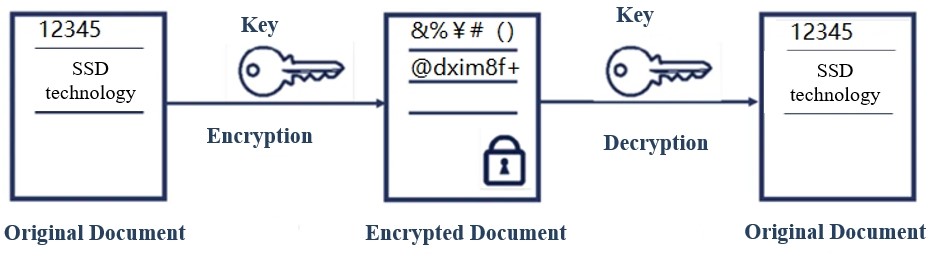
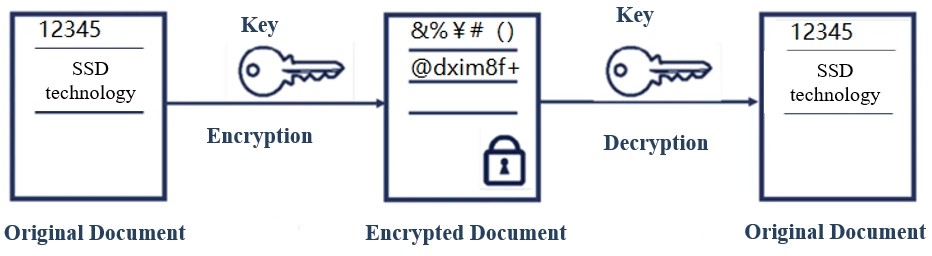
1. Symmetric encryption: refers to encryption and decryption with the same key, which is a reversible way of encryption.
At present, the mainstream symmetric encryption algorithms are as follows:
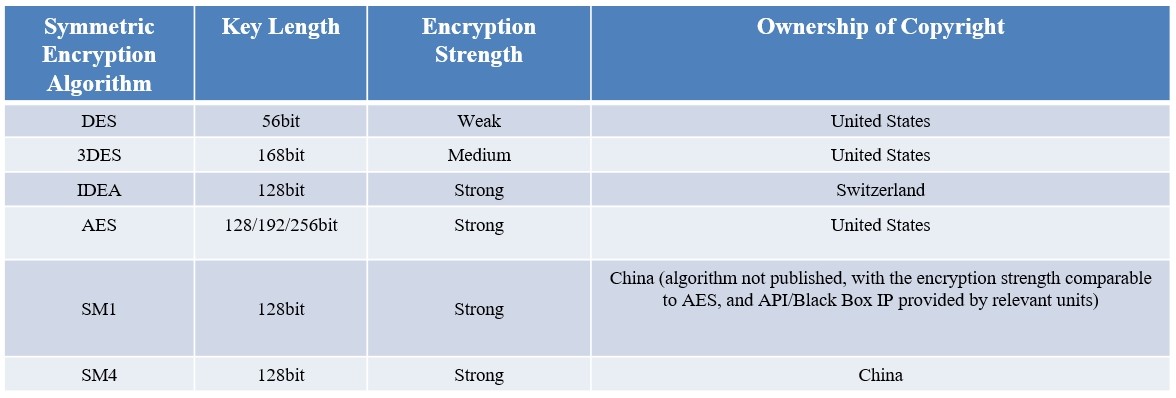
·DES: The process is to encrypt the plaintext by DES with 64 bits as a group and then generate ciphertext. Similarly, the ciphertext is divided into groups with 64 bits each group. The consecutive groups of ciphertext can be restored to the corresponding plaintext by the decryption key.
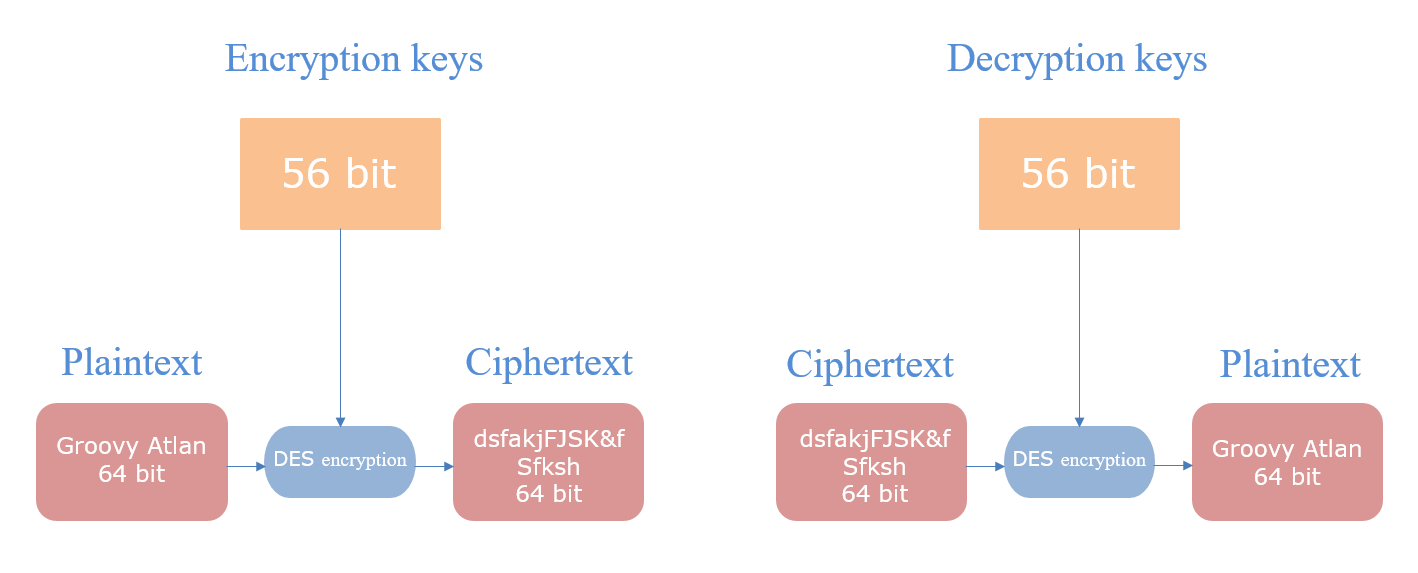
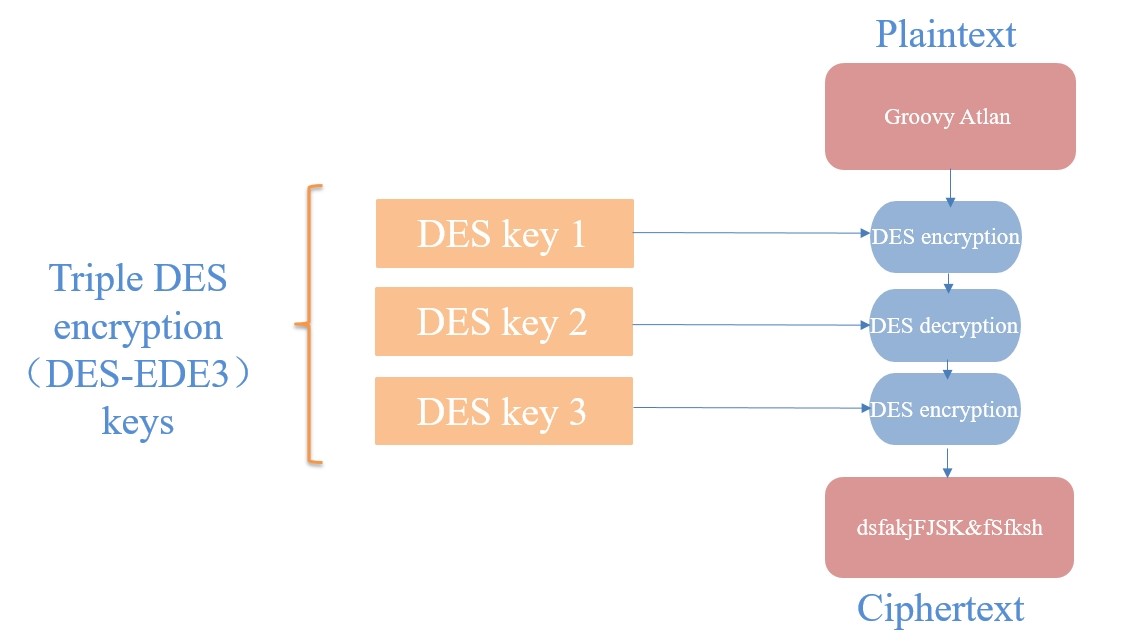
·3DES: Literally, it is the process of DES encryption for three times, which is an enhanced version of DES.
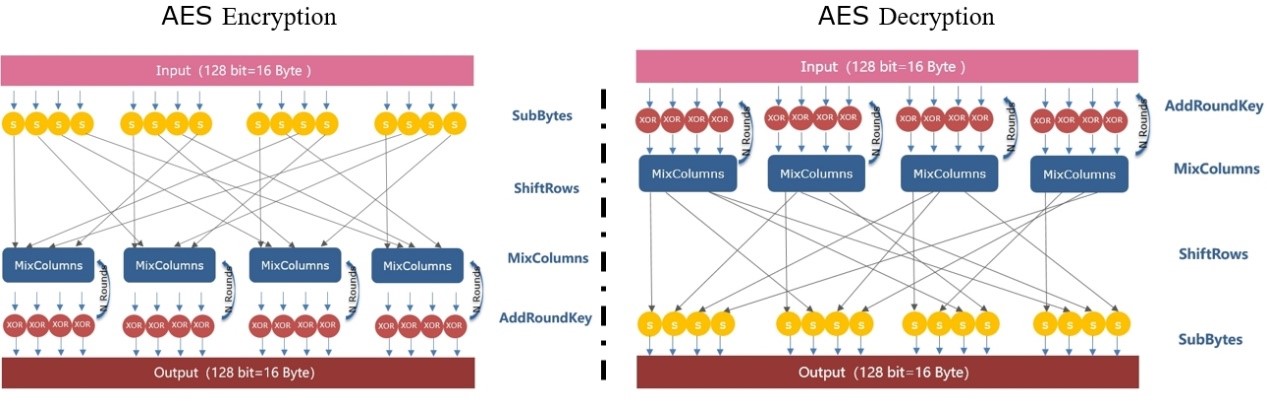
·AES: Due to the complexity of the process, it isn't explained thoroughly here. The general process is that the input plaintext data will be replaced byte by byte. After the replacement is completed, it will be translated. After completion of the translation, it will be done with N times of hybrid column iteration. Finally, it will perform XOR operation to generate ciphertext. To decrypt, operate in reverse.
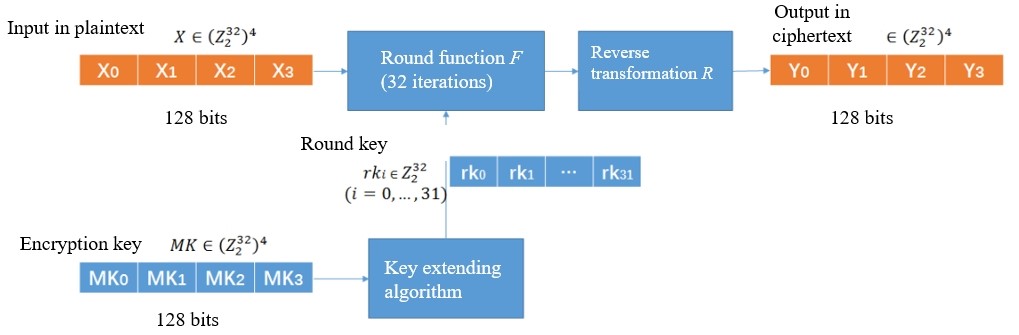
·SM4: SM4 is a block cipher algorithm with a block length of 128 bits (16 bytes, 4 words) and a key length of 128 bits (16 bytes, 4 words). With it, the encryption and decryption process adopts a 32-round iterative mechanism (similar to DES and AES), with a round key (similar to DES and AES) and a reverse transformation for each iteration.
2. Asymmetric
encryption: characterized by the fact that ciphertext cannot be inverted
into plaintext, which is an irreversible process.
The mainstream asymmetric encryption algorithms are as follows:
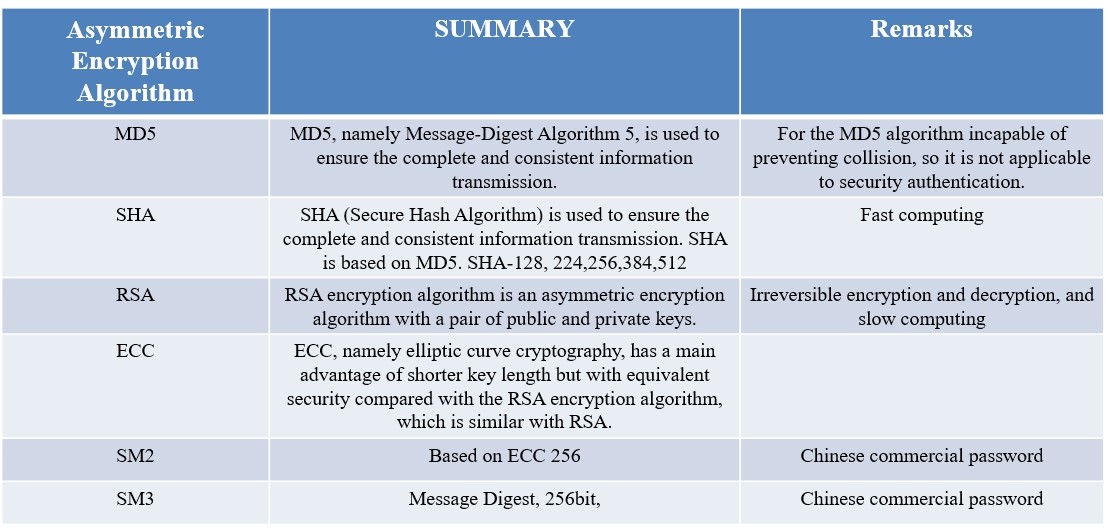
·MD5/SHA: Used for file verification and digital signature for files (to ensure the correctness of original plaintext during data and plaintext transmission). The file content can be plaintext. It can be seen from the figure below that the original text cannot be inferred from the summary data. It is often used for the online file transmission and verification.
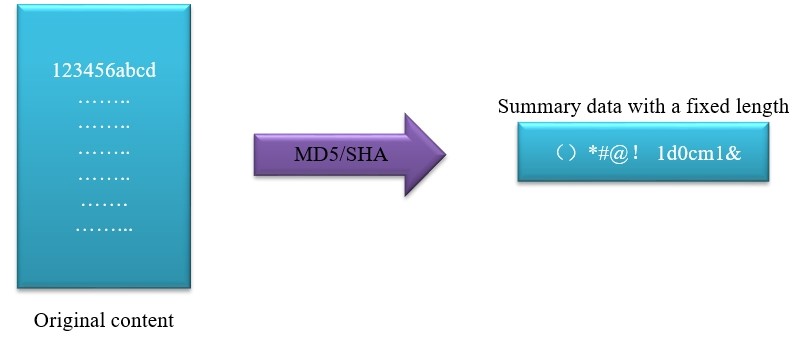
·RSA: Explained by two examples.
Example 1: Company A wants to release a public file (such as a driver file), with a public key and a private key generated. First, it uses the private key to encrypt and sign to prove that the product belongs to Company A and that the product is safe and legal. After downloading the driver file, users can use the public key to verify the signature (like Microsoft that will prompt whether this is a legal
signed driver) for normal use.
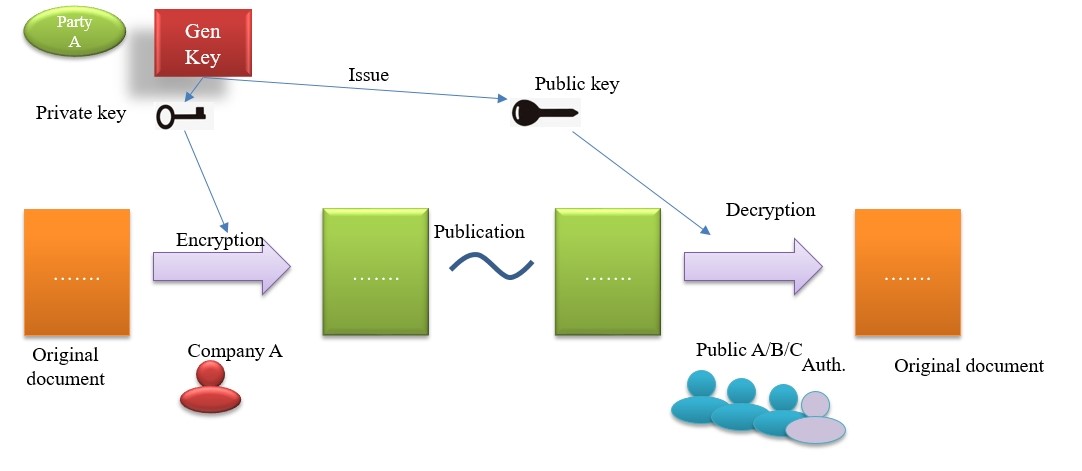
Private key for signature, while public key for verification of the signature
In fact, the process of digital signature with Microsoft applications is more complex than that shown in the figure, because the public and private keys need to be issued with a generation certificate by a third party to prove, instead of being generated by users themselves.
Example 2: A, B and C all want to send a private message to O, but they don't want their information to be seen by the other two. So, they encrypt their messages with the public key O gave them. Since the other two people don't have a private key to decrypt, only O can see A's message.
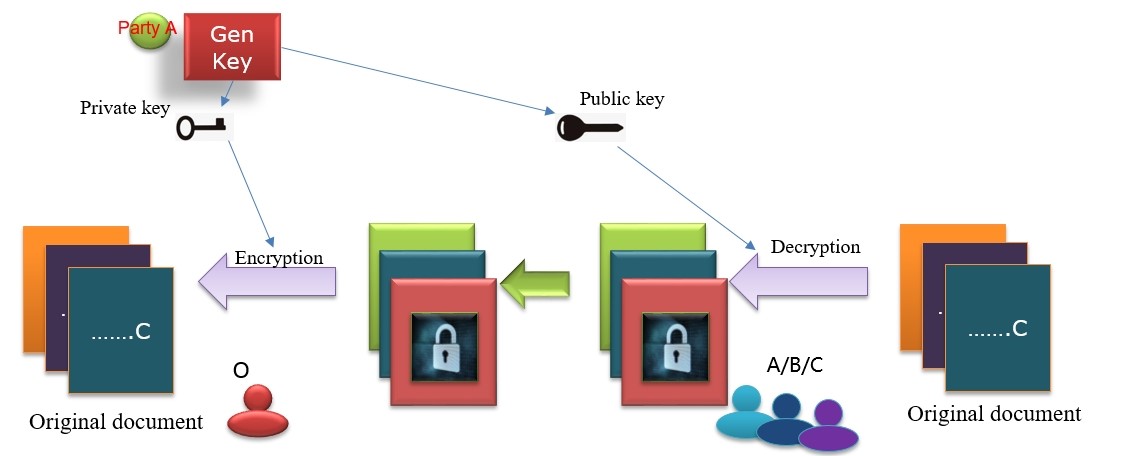
Public key for encryption, while private key for decryption and also encryption
Ⅲ. Application of encryption algorithm
In the asymmetric encryption algorithm, the private key can be used forward to release a signature and then let it to be verified. Conversely, everyone can also use the public key to encrypt a file. However, there is no reverse operation in the application in SSD.
·Application of encryption algorithm in SSD
There is an AES hardware module inside the SSD for encrypting and decrypting host or internal data. Its key is managed by the firmware of the SSD and stored on NAND or the OTP area inside the SOC. As specified in IEEE 1667, the SSDs with a built-in encryption module are called SED (Self encrypting) SSD, and others as Non-SED SSDs.
Under different implementations, some SOCs will put the AES module on the front or back end for encryption.
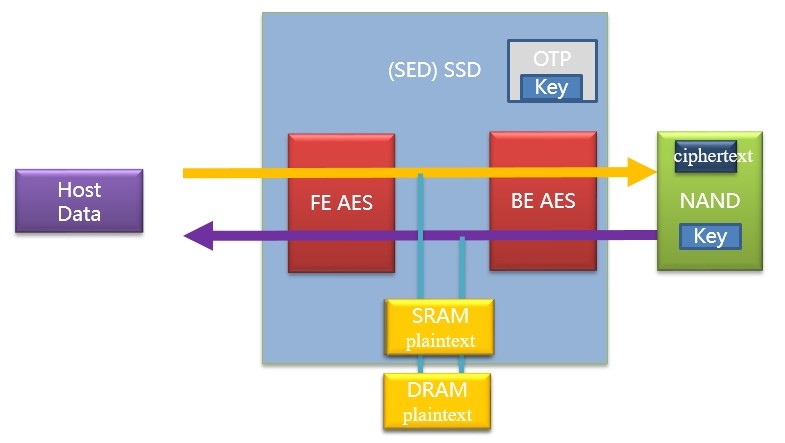
Ⅳ.ATA security
Those described above are all encryption algorithms. At a higher level, such as the system application layer, security mechanisms such as key management and account login are required for authentication.
ATA (AT Attachment), a very old standard, defines a set of storage command interfaces for access to storage devices (SSD/HDD).
ATA security feature: it is similar to the Windows access password. Entering a correct access password allows the entire SSD space to be read and written. Otherwise, the SSD will reject the host's read and write requests or other special application requests, so as to ensure the SSD to work in a secure environment.

ATA Security has two passwords:
·User password: Used to restrict the access to SSD, including some control commands and data read and write commands. Generally, the BIOS login requires entering a password, that is, the User password, to unlock the SSD.
·Master password: Administrator password, only used to unlock the User Password without locking the hard disk; the Master password does not enable SSD security.
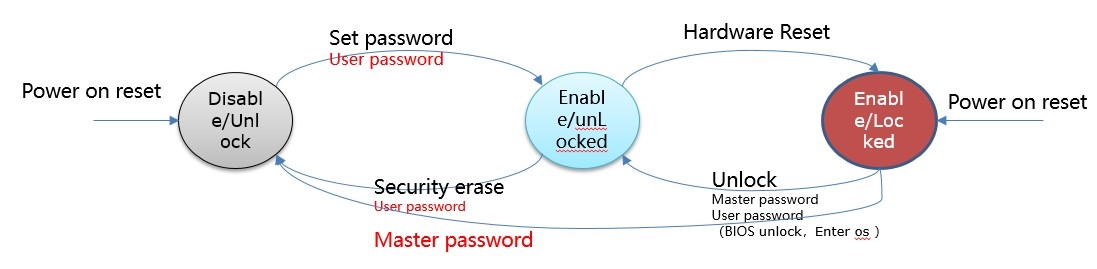
Diagram of Security State
Security erase:
1. Normal erase;
2. Enhance erase.
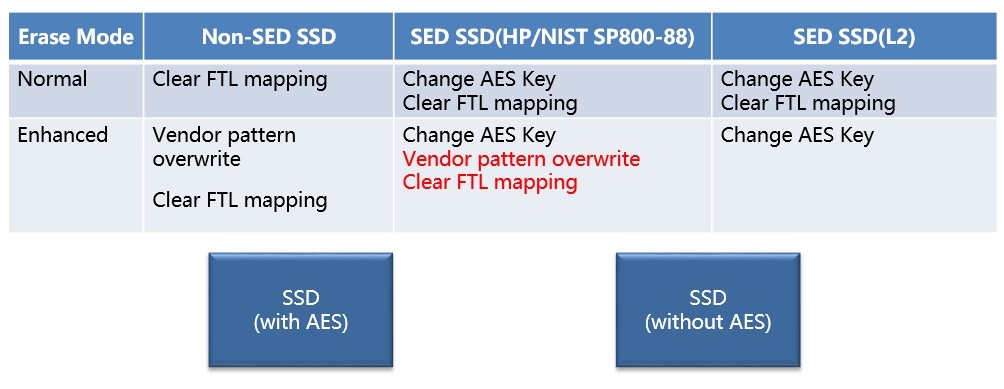
Difference between SSDs with and without AES
Ⅴ.TCG
Trusted Computing Group (TCG) was originally developed by AMD, HP, IBM, Intel, and Microsoft to establish the concept of trusted computing for personal computers. Rather than merely a hard disk encryption method, it is also an IT ecology, integrating network, storage, encryption hardware modules, basic platforms, software, etc.
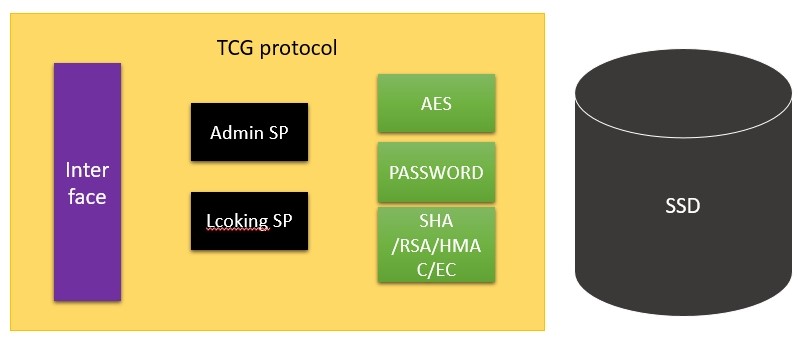
In TCG, the part related to SSD is the TCG Storage protocol.
As shown in the figure, there are two SPs above the SSD: Admin SP and Locking SP. Admin SP, similar to the administrator permission set, has only some management functions. It is not used for the allocation of the SSD's logical space or for decision-making; while Locking SP is used for SSD access space management.
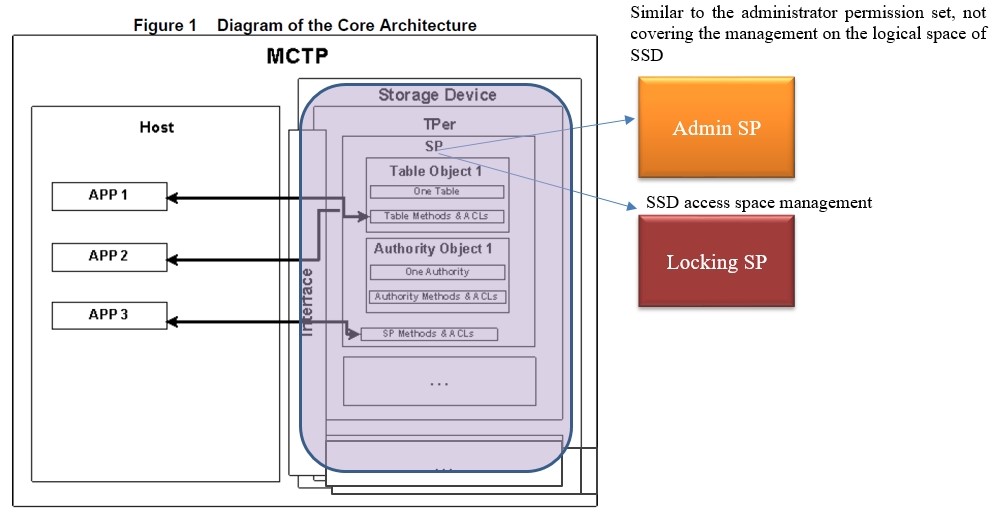
TCG Storage integrates the encryption technologies introduced above to manage SSD authorization and data security.
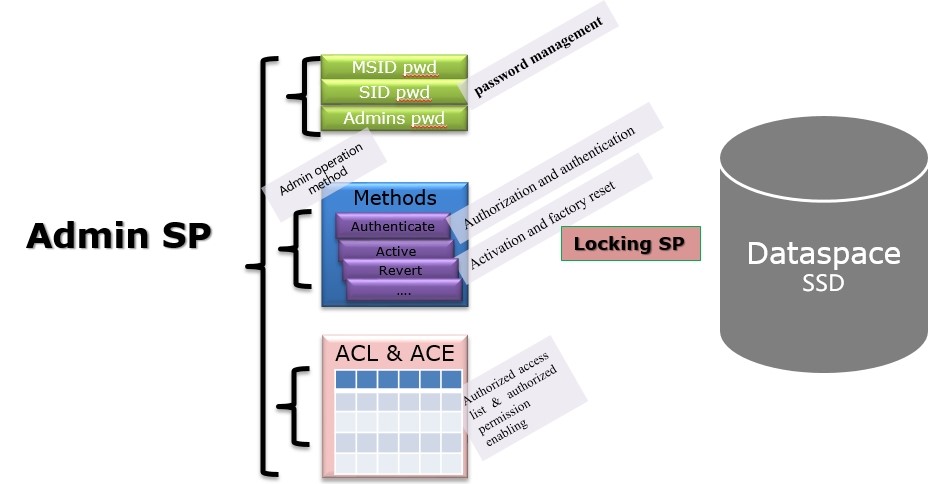
Between them, Admin SP is the most important and used for password management, enabling/disabling the Locking SP, restoring factory settings, etc. Admin SP is generally used for management of dozens of types of passwords, and does not directly manage the SSD data space.
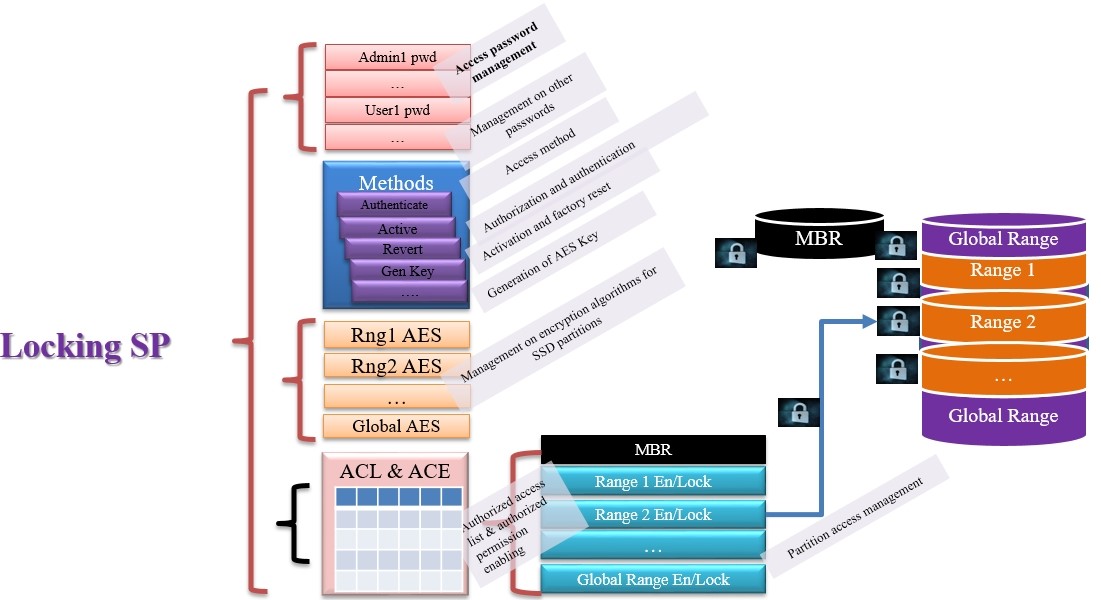
In addition to the basic feature of management, Locking SP is also in charge of management for data spaces, such as space partitions, encryption of each partition, independent partition locks, and access passwords.
Ⅵ. Hidden partition
·TCG MBR shadow
This MBR is not the Master Boot Record in the OS. The MBR in TCG overlaps with the user space, and only one of them is visible to the host at the same time. Before the SSD is fully authorized, the real User data space cannot be accessed, but only a small space displayed to the host, where some Preboot authentication programs and data are stored. After successful authentication, the system will switch to the real User data space.
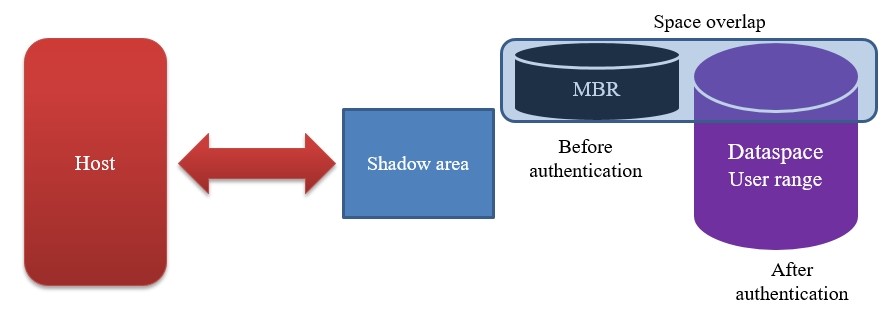
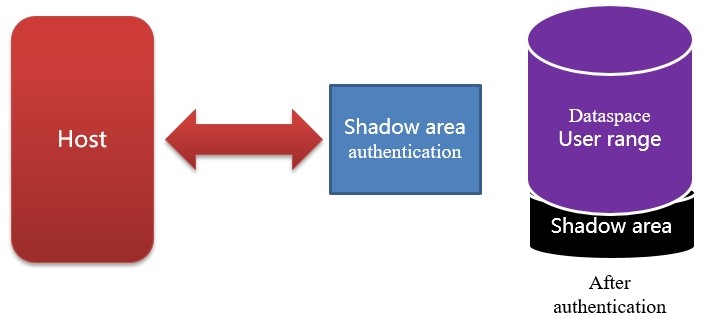
·Shadow area:
An additional area created in the SSD physical space, which is invisible to the Host before authorized. Otherwise, it will be visible to the Host. It is generally used to store some data of the host manufacturer and to back up and restore some data required by the host manufacturer. Compared with TCG, it will occupy some of the user's physical storage capacity.
SSD products developed by UnionMemory support all the current standard encryption algorithms in the industry. Related encryption algorithms could be used to encrypt user data and the firmware package signature before release, so as to ensure the firmware not to be maliciously tampered after release, thus further guaranteeing the security of SSD. At present, the encryption technologies adopted for SSD products of Union Memory are all industry-leading, which can build a solid barrier for data security.